Synology Active Backup for Server
Introduction
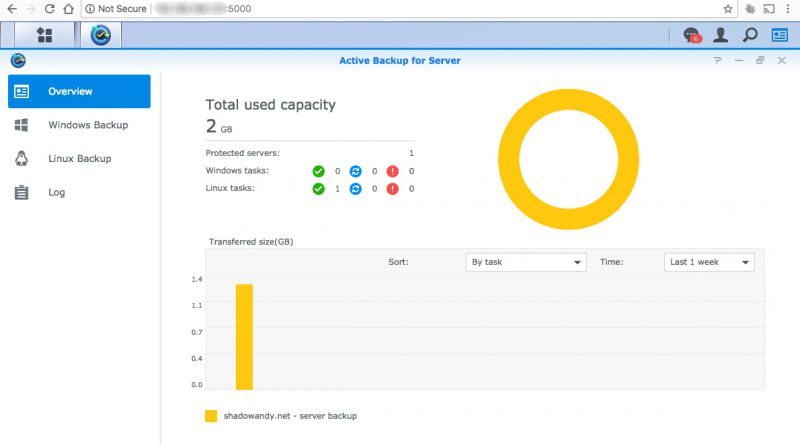
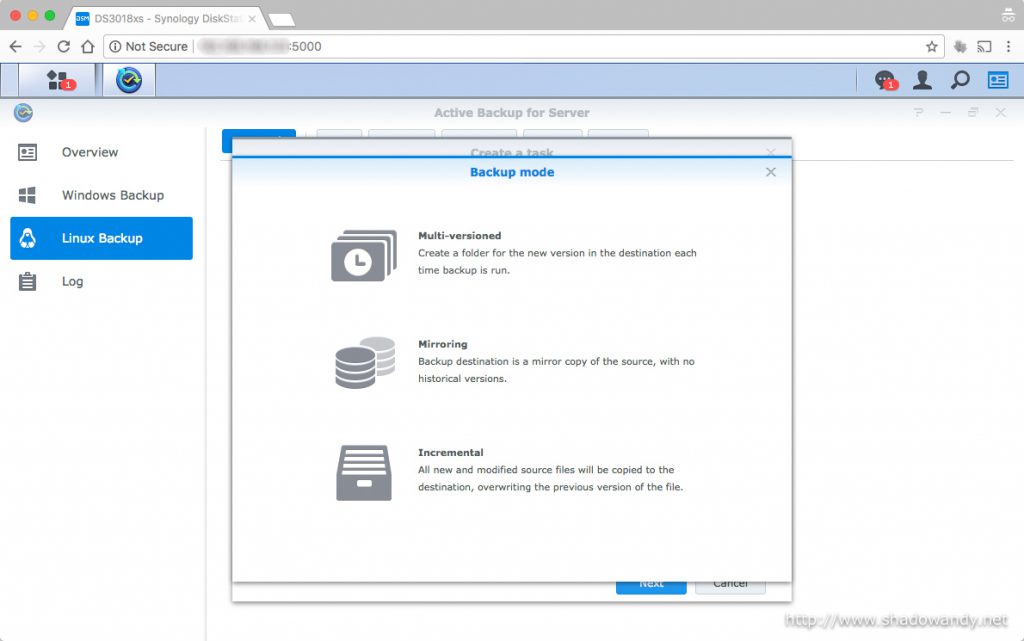
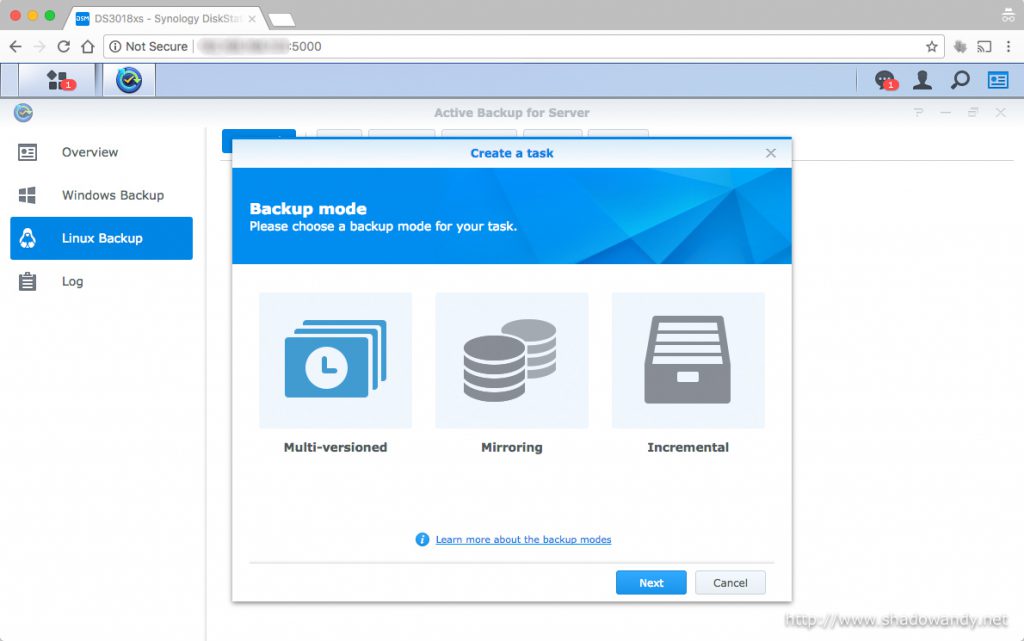
Synology’s Active Backup for Server is a package specially designed to centralize data backups for Windows and Linux servers. It support backup modes like multi-version, mirroring and incremental. The source servers need not install additional backup agents as it uses SMB or rsync to perform the backups. Active Backup for Server is available on DSM 6.0 – 7185 and above versions. I was looking for a remote backup solution for my Amazon Lightsail virtual private server and Active Backup for Server seems to be up for the task.
A little background into Amazon Lightsail
Amazon Lightsail offers an easy-to-use platform to launch and manage virtual private servers (VPS). Both Windows and Linux VPS are available. In the backup department, Amazon Lightsail allows me to do a snapshot of the instance.
Being a VPS, I have (almost) full administrative control, including remote shell access. With remote shell access, I can probably do an off-site backup of the VPS’s data to my Synology DS3018xs or DS1817+ using Synology Active Backup for Server.
What is required to backup a Linux server?
There are some basic prerequisites before you can backup a Linux server using Synology Active Backup for Server. Most-if-not-all Linux server would have all these in their basic offerings.
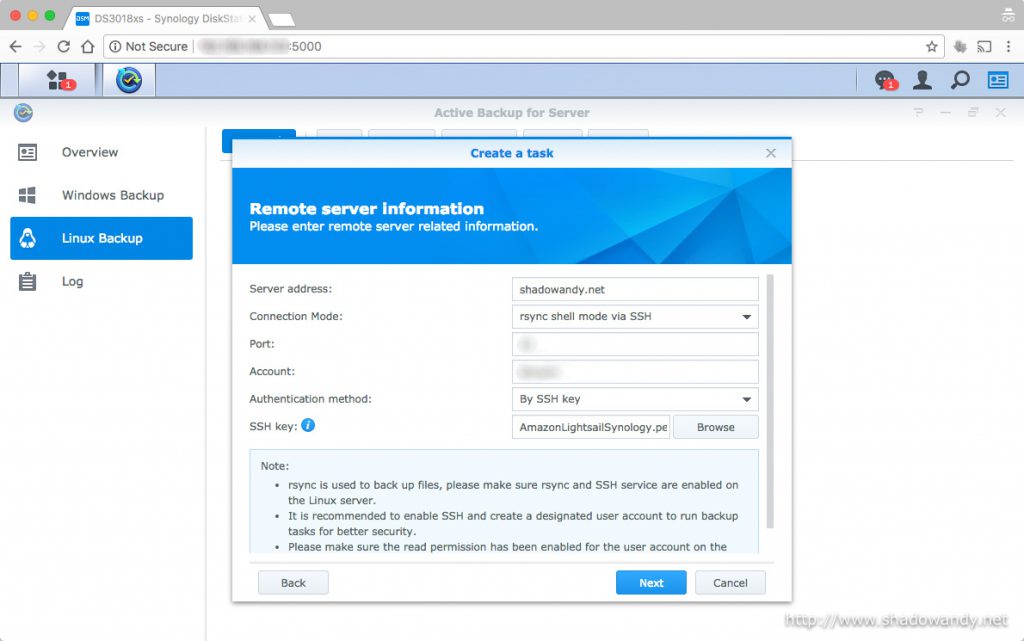
As it is using rsync as the data synchronization and backup tool, your server will need to support one of the following connection modes:
- rsync module. Essentially the rsync daemon running on the server to be backed up. This mode does not support transport encryption.
- rsync shell mode over SSH. Basically running the rsync command in a shell window between two folders (and sub-folders). The SSH would provide transport encryption.
- rsync module mode over SSH. This seems to tunnel the connection to the rsync daemon over SSH. The SSH would provide transport encryption.
Other than the connection mode, the server need to support at least one of the following authentication modes:
- Password. This is required for rsync module and SSH access (if you are using it).
- SSH key. It also support SSH authentication via SSH key. However, you cannot use a passphrase protected SSH key.
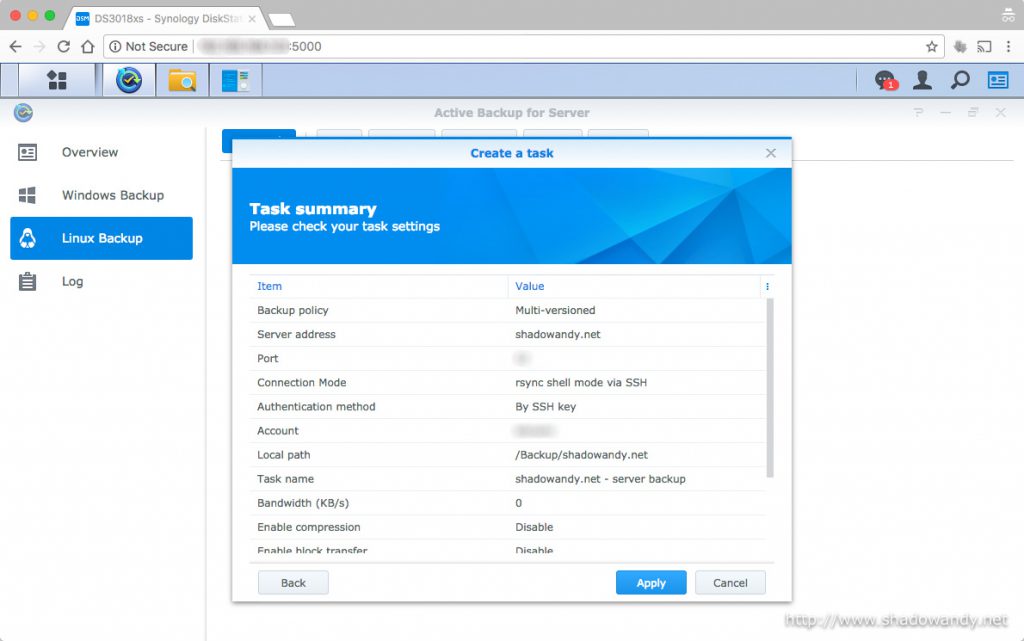
Got all the prerequisites settled? It is time to explore Synology Active Backup for Server.
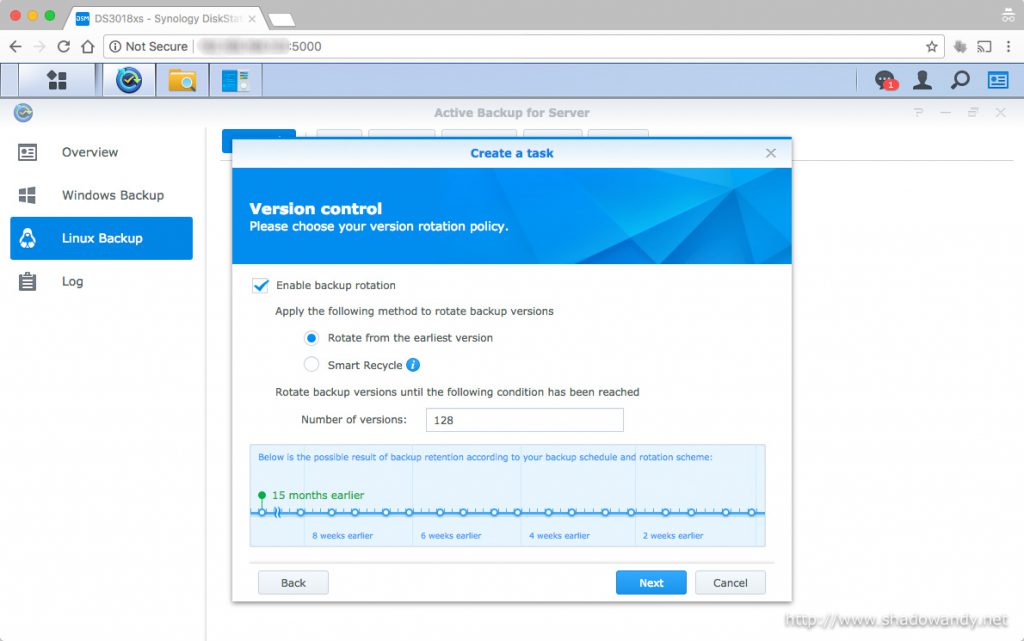
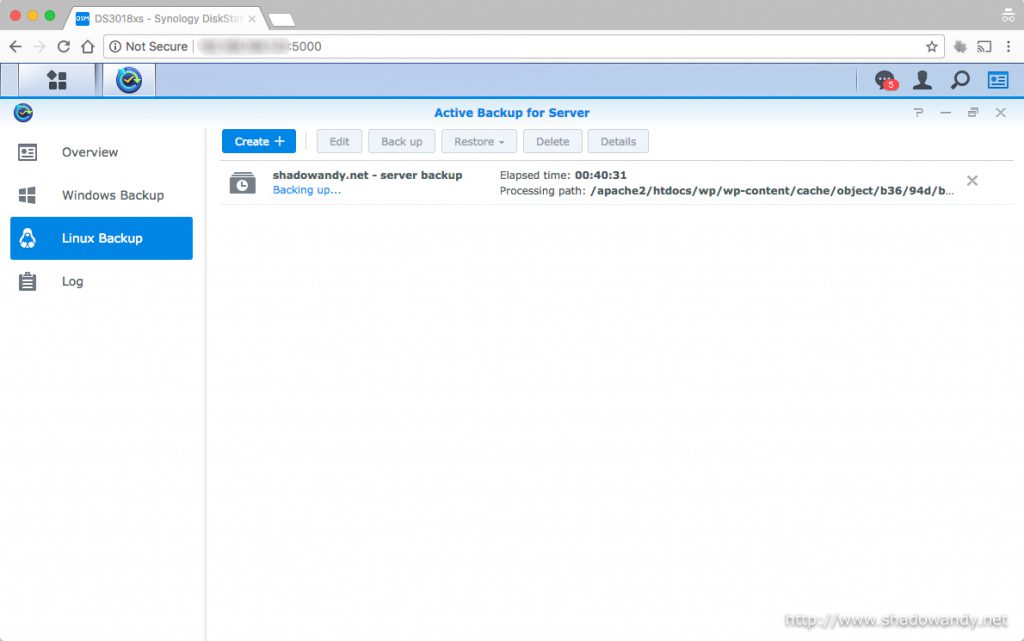
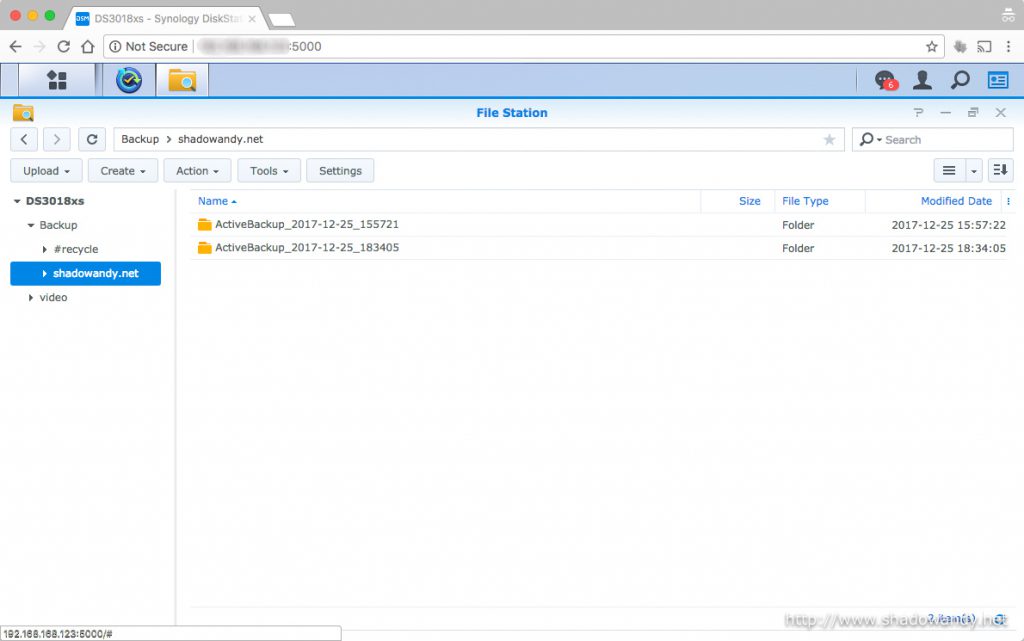
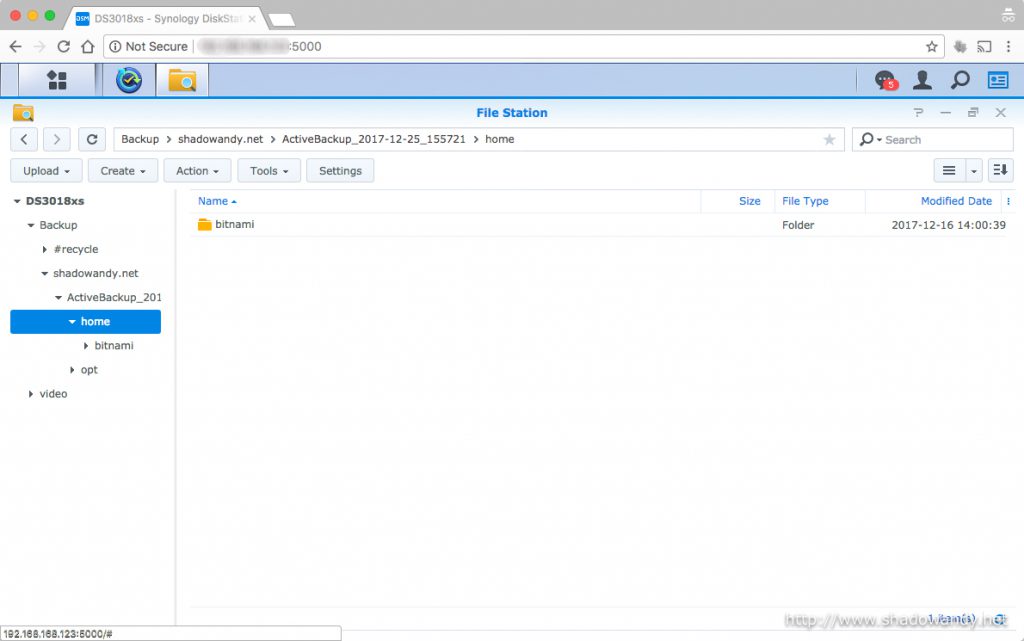
Setting up Active Backup for Server
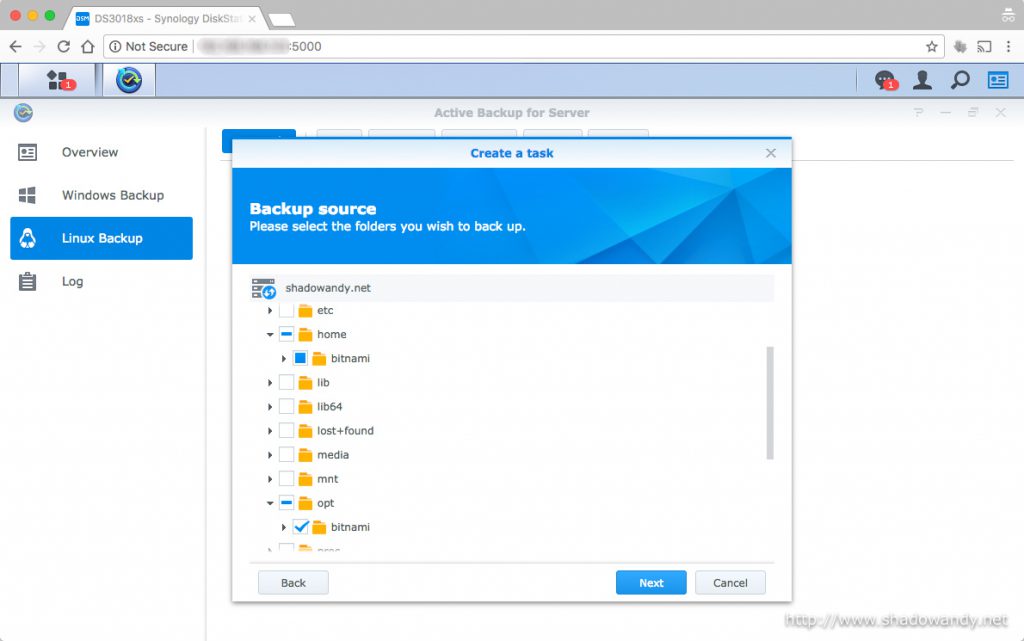
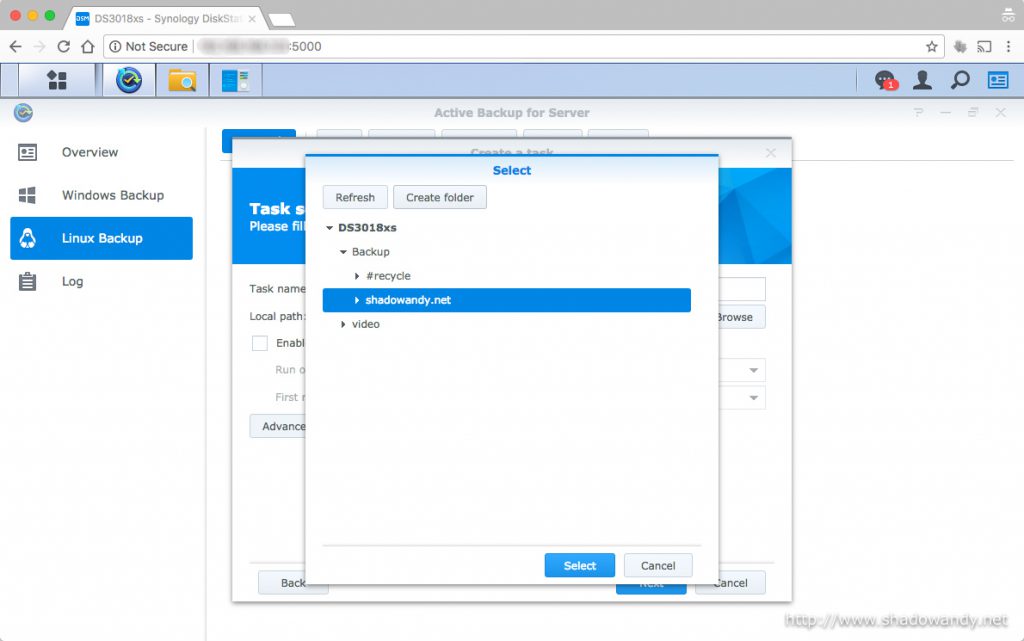
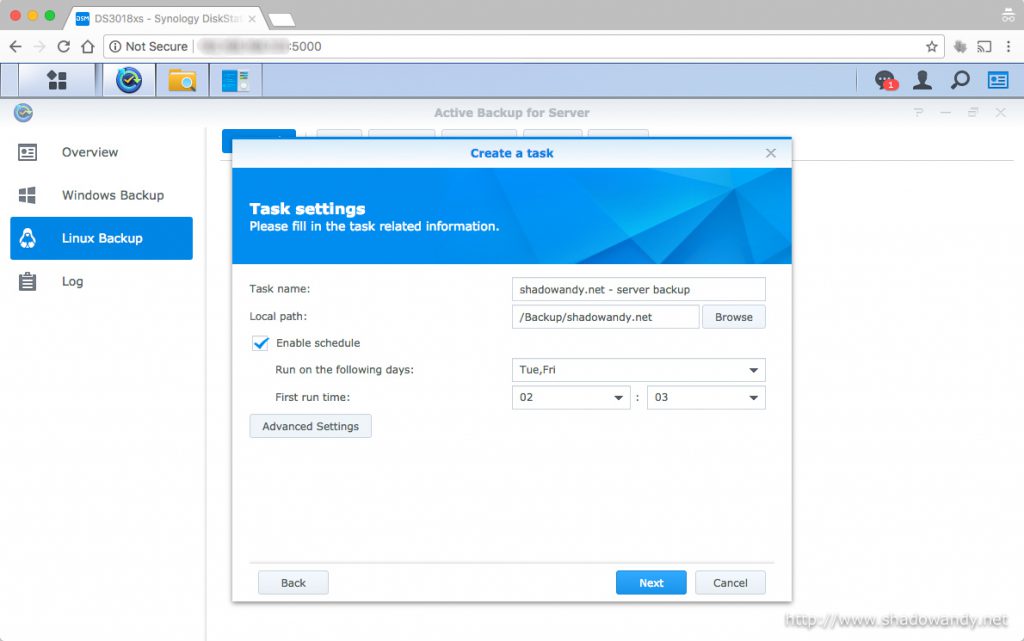
Conclusion
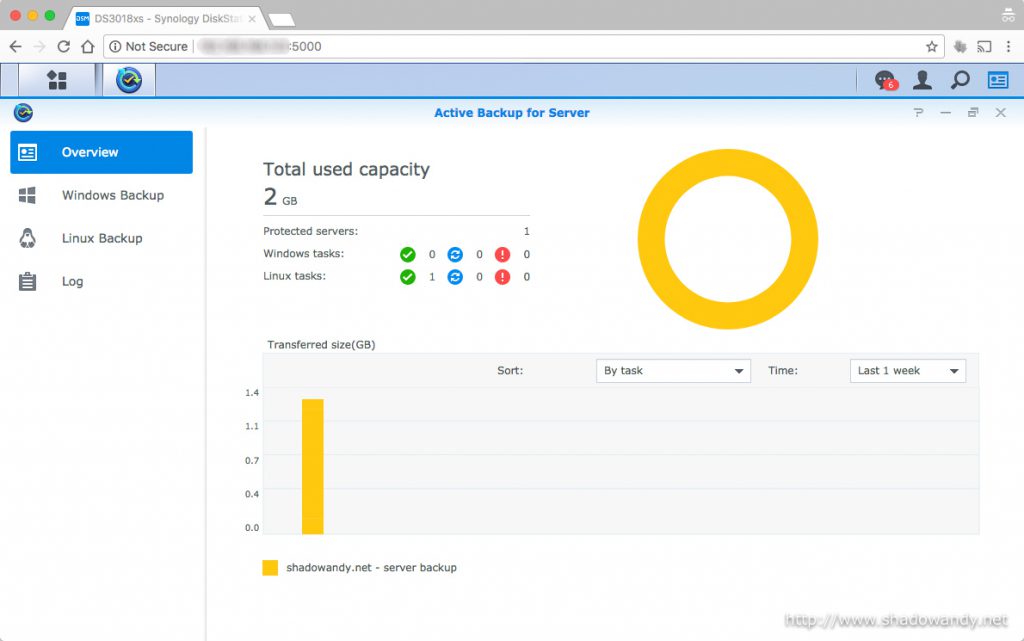
Synology Active Backup for Server is free and it offers basic and cost-effective agent-less backup solution. It also supports Windows platform by backing up via SMB protocol.
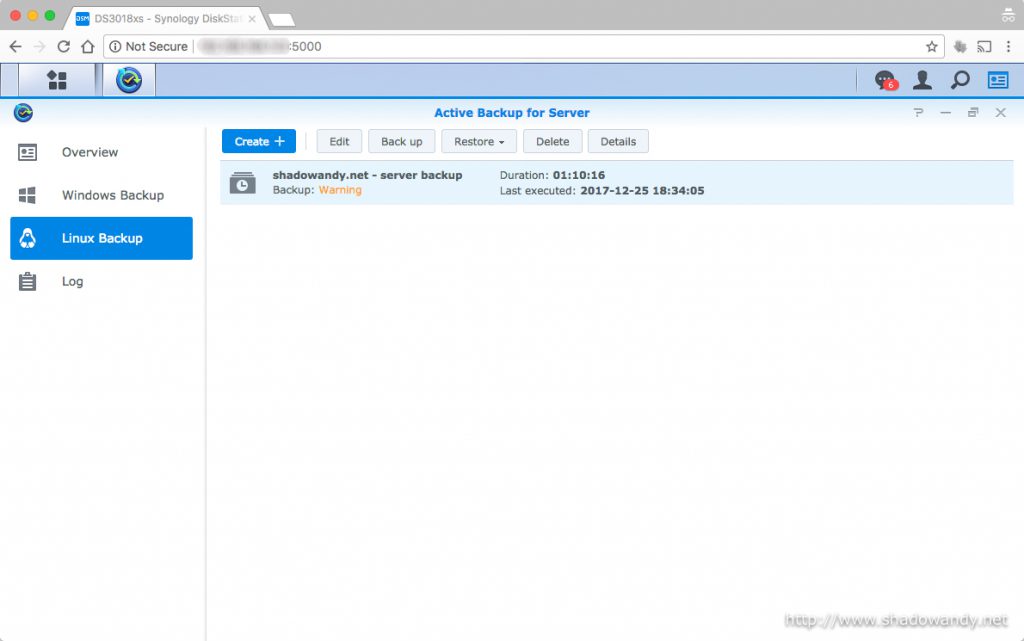
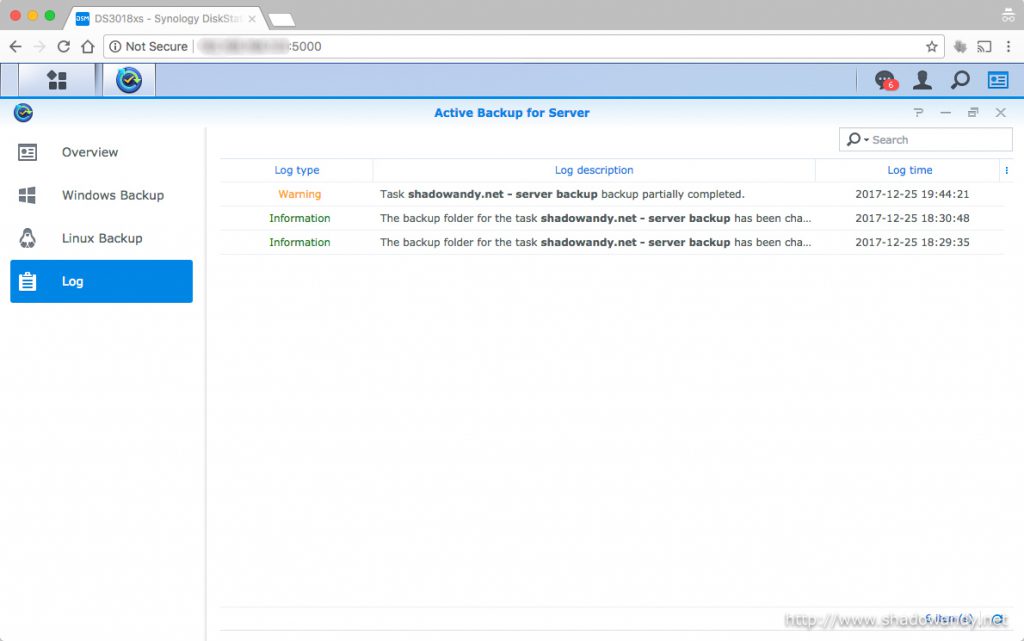
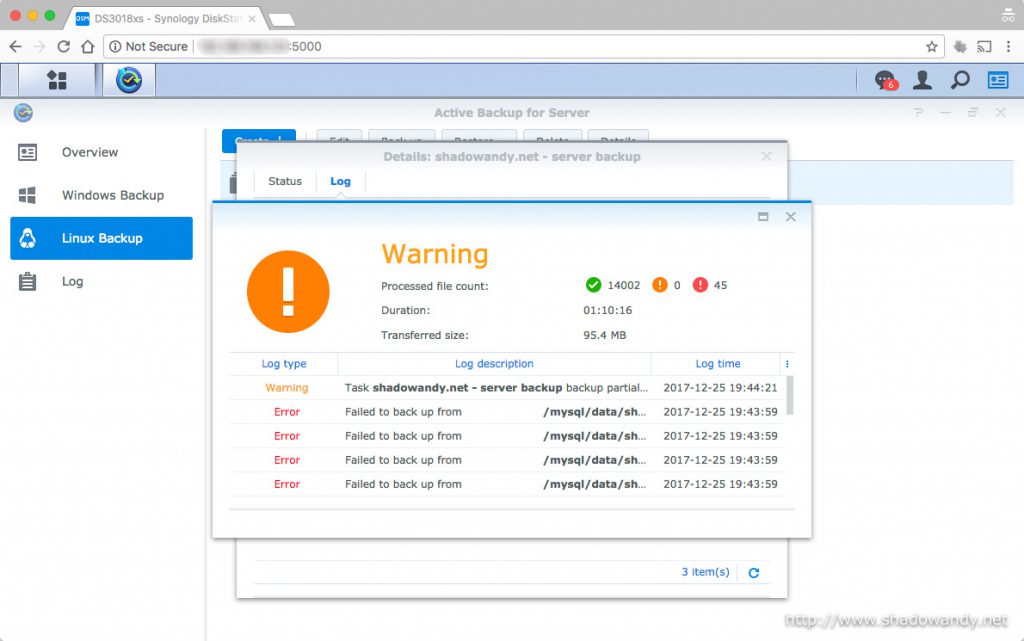
One thing that you might want to take note of is that it is unable to backup files that are currently in use (or locked by other processes). This problem is not unique to Active Backup for Server. So you will encounter issues with database files, office documents, etc. currently opened for access (or edits).
If you are backing up a server running a database instance, you might want to exclude the database directories from the backup task and dump out the database(s) into a directory for the backup task to consume. Do note that storing password in shell script is not recommended.
DBUSER="db_username"
DBPASSWORD="db_password"
OUTPUT="/my_db_dump_path"
TMP_DB_HOLDER=""
databases=mysql -u $DBUSER -p$DBPASSWORD -e "SHOW DATABASES;" | tr
-d "| " | grep -v Database
for db in $databases; do
if [[ "$db" != "information_schema" ]] && [[ "$db" != "performance_schema" ]] && [[ "$d
b" != "mysql" ]] && [[ "$db" != _* ]] ; then
echo "Dumping database: $db"
mysqldump -u $DBUSER -p$DBPASSWORD --databases $db > $OUTPUT
/$DATENOW.$db.sql
TMP_DB_HOLDER="$TMP_DB_HOLDER $OUTPUT/$DATENOW.$db.sql"
fi
done
tar -zcf $OUTPUT/$DATENOW.sqldump.tar.gz $TMP_DB_HOLDERRestoring the contents is as simply as selecting the task, choosing the folders (or files) and restoring them to:
- Custom location and overwriting any files in the location with the same name; or
- Custom location and skipping any files in the location with the same name; or
- Original location and overwriting any files in the location with the same name; or
- Original location and skipping any files in the location with the same name.
Lastly, Synology Active Backup for Server does what it is supposed to do. According to Synology’s page on Active Backup for Server, there will be a premium edition with advanced features will be released in the future with consideration of different workloads, enhance data backup and improved restore efficiency.